Scaling Unleash for enterprise workloads
When evaluating Unleash for enterprise-wide adoption, your primary concerns likely revolve around scalability, performance, and availability. You need assurance that your chosen feature management system can handle potentially tens of millions of users and millions of flags across a number of regions, without compromising user experience or introducing system fragility.
This guide explains how Unleash is architected to meet these demands, focusing on:
- Global scale: Handling distributed traffic efficiently across multiple regions.
- Resilience: Ensuring high availability and fault tolerance to prevent outages.
- Performance: Delivering low-latency flag evaluations for a seamless user experience.
We’ll explore the core architecture of Unleash and the mechanisms that enable effective scaling, ensuring high performance and resilience, even under significant load. We will cover deployment options, reference architectures, and best practices for enterprise environments.
Unleash core architecture
Unleash is fundamentally designed for speed and resilience. Understanding the core principles of the architecture is key to grasping how it scales effectively.
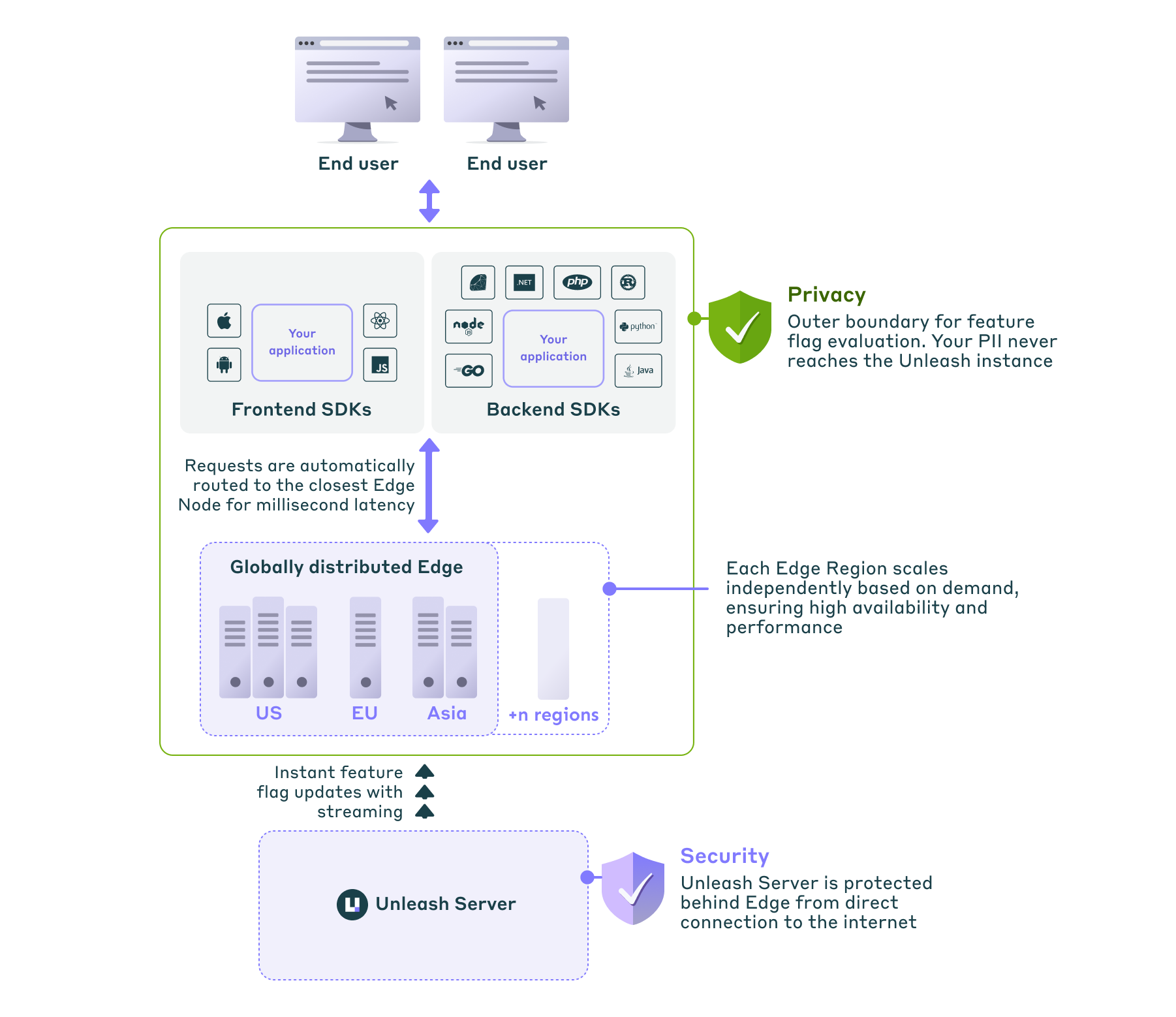
Fast, local feature flag evaluation
SDKs embedded in your applications fetch feature flag configurations from the Unleash server or Unleash Edge.
Backend SDKs perform flag evaluations locally within the application’s memory. This eliminates network latency for each evaluation, resulting in extremely fast checks.
Frontend SDKs rely on Unleash Edge as a fast, lightweight caching and evaluation layer closer to the end-user.
Resilience through caching
SDKs enhance resilience by caching the last known valid configuration. For optimal performance, this is often kept in-memory, but SDKs can also be configured to use persistent backup storage (like a local file, Redis, or S3). If the Unleash API server or Unleash Edge becomes temporarily unavailable, the SDK continues operating using these cached flags along with predefined default values. This persistence ensures your application remains functional not only through network interruptions but also allows it to recover state even after restarting during an upstream outage.
For a deeper dive, explore the Unleash architecture overview.
Choosing the right deployment option
How you set up Unleash to scale depends significantly on the hosting option you choose. Unleash offers flexible deployment models to match your operational preferences and requirements. Let’s recap the three main options.
Unleash Cloud
Unleash self-hosted
Hybrid
- How it works: Unleash manages the entire infrastructure stack (Unleash API server, database, Admin UI, Unleash Enterprise Edge) on a robust, multi-region AWS setup designed for high availability and performance.
- Ideal for: Teams wanting to focus on feature delivery, minimize operational overhead, and leverage Unleash’s expertise in scaling and managing the platform. Offers the fastest time-to-value.
- Scaling and infrastructure: Automatic scaling, Multi-Availability Zone (AZ) deployments, managed databases with automatic failover, and built-in disaster recovery. Handles traffic bursts seamlessly. Leverages a globally distributed Unleash Edge network for low latency.
- Key tradeoff: Less direct control over the underlying infrastructure compared to self-hosting, in exchange for significantly reduced operational overhead.
Scaling Unleash
Let’s look at the key considerations for scaling the Unleash API server, its database, and the Admin UI.
Unleash API server
This component is a Node.js-based, stateless API. It can be scaled horizontally by running multiple instances behind a load balancer, ideally across different Availability Zones (Multi-AZ).
Utilize Auto Scaling Groups (ASGs) or similar mechanisms in cloud environments to automatically adjust capacity based on load metrics (such as CPU utilization, memory usage, request count).
Database
A PostgreSQL database that stores all configurations, feature flags, strategies, context fields, metrics, and audit logs. It is the critical stateful component.
The database layer must be performant and highly available. Use managed database services (such as AWS RDS for PostgreSQL) configured for high availability and backups.
Unleash Frontend / Admin UI
A bundled single-page application interface for interacting with the Unleash API server. Use a global content delivery network (CDN) to serve the UI and static assets for fast loading times worldwide.
How we scale Unleash Cloud
Unleash achieves scalability and high availability by distributing API instances, ensuring database resilience, providing regional disaster recovery, utilizing a CDN for UI assets, and dynamically handling traffic bursts. Let’s look at the key mechanisms at play.
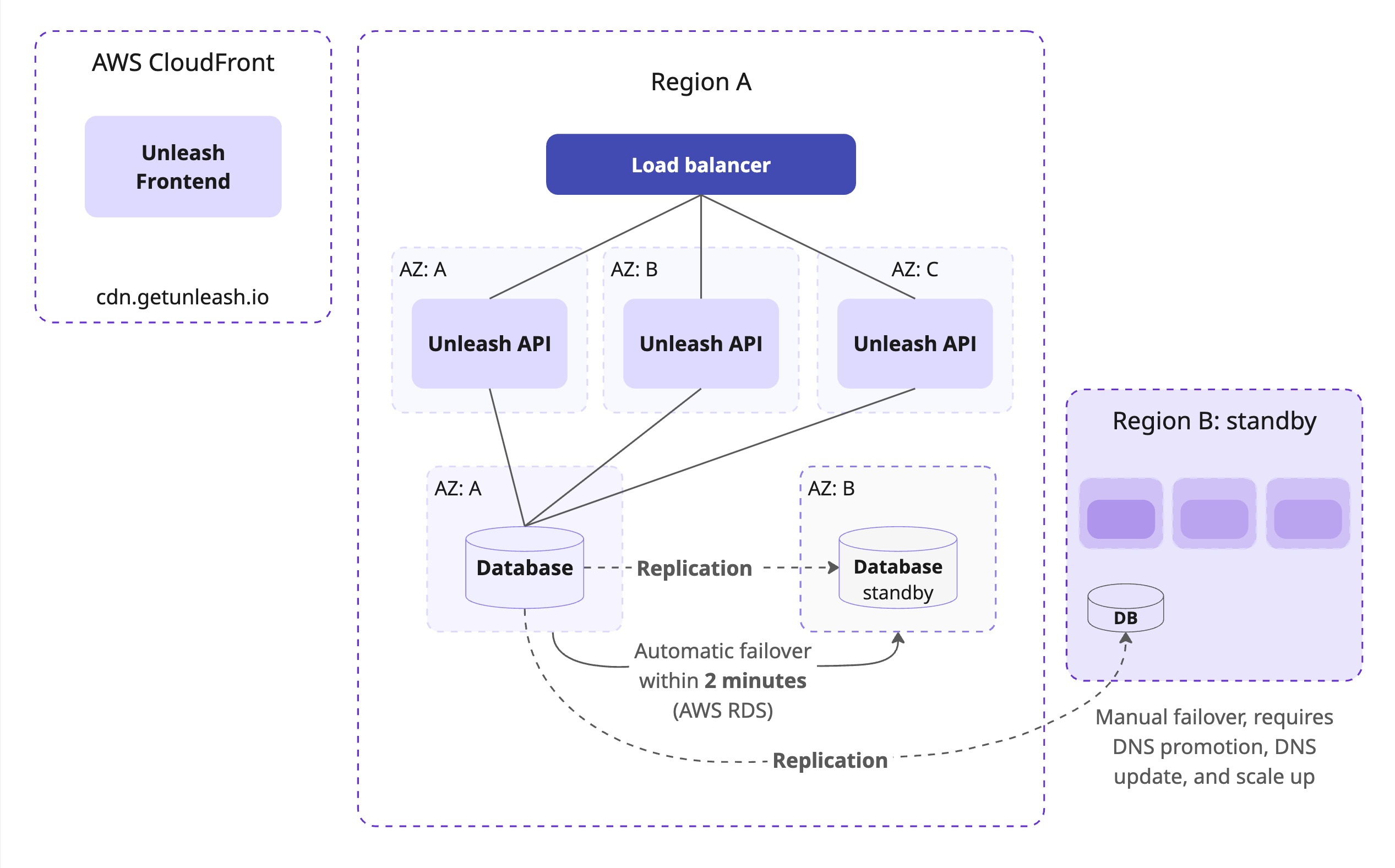
Horizontal scaling
We run Unleash API instances across multiple AWS Availability Zones (Multi-AZ) in each region. Load balancers distribute incoming traffic, and our infrastructure automatically scales compute resources, allowing the number of Unleash instances to adjust based on observed load.
Database resilience
We use AWS RDS for PostgreSQL configured for high availability with Multi-AZ deployments, providing automatic failover within 2 minutes to a hot standby in case the primary database instance or its AZ fails.
Regional disaster recovery
Full backups are stored in a separate region. A standby Unleash cluster in the backup region can take over in the rare event of a complete primary region failure.
CDN for UI assets
The Unleash Admin UI is served through a global CDN for fast loading worldwide.
Handling bursts
Our managed environment is designed for elasticity. Auto-scaling adjusts resources automatically. We continuously monitor load and performance metrics, allowing the system to handle sudden traffic peaks, such as those from product launches or marketing campaigns, ensuring consistent performance.
Self-hosting Unleash: Designing for high availability
When designing for high availability and resilience in a self-hosted environment, we recommend that you implement the following strategies:
Multi-AZ deployments
We recommend running the Unleash API nodes in at least two different Availability Zones within a single region. Place these instances behind a load balancer that distributes traffic across the healthy instances in different AZs.
Key benefits:
- Reduces single point of failure within a region.
- Supports zero-downtime maintenance and upgrades.
- Allows for auto-scaling based on CPU/memory or request latency.
Databases and replication
For enterprise-scale deployments, a robust, managed service (such as AWS RDS for PostgreSQL) is recommended.
Configure the following:
-
Multi-AZ deployment for automatic failover within the primary region.
-
A cross-region read replica or continuous backups shipped to a secondary region for disaster recovery purposes.
-
Point-in-time recovery (PITR) to handle accidental data deletion or corruption scenarios.
Handling failover
SDK caching provides resilience against temporary database unavailability for flag evaluations, but we still recommend that you configure high-availability for the database to maintain key functionality like flag configuration updates and Admin UI access.
Configure automatic failover for your database (managed services typically handle this). Failover within a region should ideally complete in less than a few minutes. Ensure full database backups are regularly taken and stored securely, preferably in a separate region.
In the rare event of a complete primary region failure (disaster recovery scenario):
- Promote the database read replica (or restore from backup) in the standby region to become the new primary database.
- Adjust DNS records or load balancer configurations to direct traffic to the Unleash API instances in the new region. DNS propagation latency could be a limiting factor on your ability to recover.
- Scale up compute resources (API servers, Edge instances if applicable) in the new region as needed to handle the full production load.
Scaling with Unleash Edge
For organizations with globally distributed users and a high number of frontend flag evaluations (in web applications and mobile apps), relying solely on the Unleash API server can introduce latency for end-users and place significant read load on the API server and database.
Unleash Edge acts as a lightweight, globally distributed, read-only caching layer for your feature flag configurations. SDKs connect to the nearest Edge instance instead of directly to the Unleash API server.
Edge was specifically built to handle scenarios where tens of millions of end-users are spread across the globe, requiring localized evaluation of feature toggles with minimal latency.
Why use Edge?
- Low latency: Dramatically reduces flag configuration fetch times for users worldwide by serving requests from a geographically closer point. With Enterprise Edge, feature flag updates are pushed instantly from the Unleash server to the Edge nodes, ensuring they are always up-to-date.
- Scalability: Edge instances are stateless and optimized for high throughput. They can be scaled horizontally, independently of the Unleash API server. This offloads the vast majority of read traffic (SDK polling/requests) from your Unleash API server and database. A single Edge instance can typically handle tens of thousands of requests per second.
- Enhanced availability: Edge instances maintain an in-memory cache of the flag configuration. If the Unleash server is temporarily unavailable, Edge continues to serve the last known valid configuration to SDKs, providing an additional layer of resilience beyond the SDK’s own cache.
Global scale and multi-region scenarios
When you require low-latency flag evaluations for a globally distributed user base, we recommend that you use distributed Edge instances across multiple global regions.
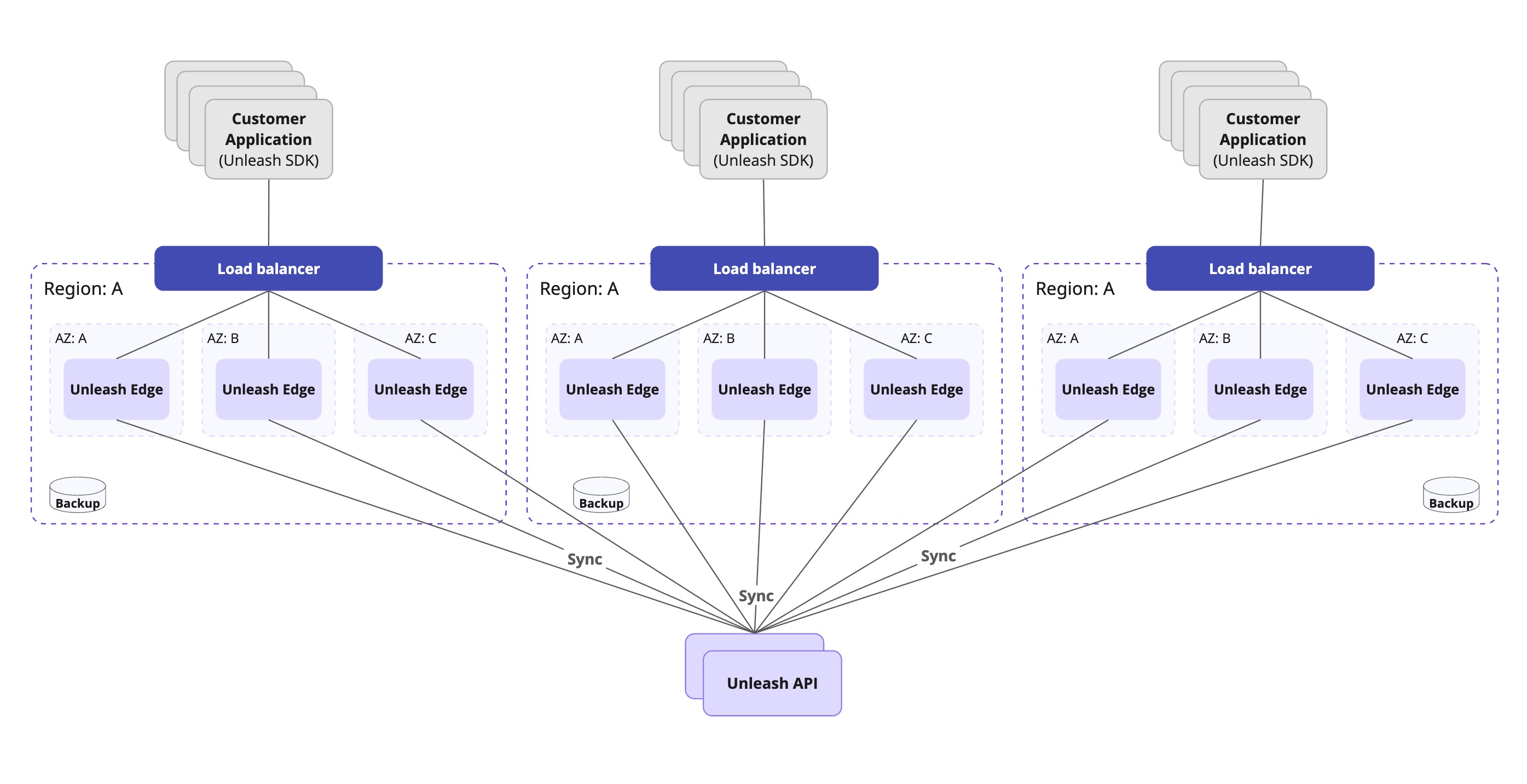
With Unleash Enterprise Edge Cloud, this complexity is handled for you—you simply configure your SDKs with the provided Edge URL. We ensure that:
- Edge instances run across multiple global regions with at least two AZs within each region.
- SDKs automatically connect to the nearest available region. Traffic fails over to other regions if one region becomes unavailable.
- Edge nodes are always up to date due to streaming, SDKs connected to Edge can continue evaluating flags even if the connection to the primary Unleash API server is temporarily lost.
Lower scale or single-region scenarios
Even when global scaling and minimizing cross-region latency are not immediate priorities, implementing high availability is crucial for reliable production workloads using Unleash.
A standard approach involves addressing potential single points of failure within a region:
- Deploy redundant API instances: Run multiple Unleash API instances across different Availability Zones (AZs). Place these instances behind a load balancer. The load balancer distributes traffic and routes requests away from failed instances or AZs, maintaining application-level availability.
- Use a multi-AZ database: Configure your managed database service (such as AWS RDS for PostgreSQL) for multi-AZ deployment. This provides data resilience and automatic failover for the database layer.
- Configure your SDKs: Set SDKs to connect to the Unleash server via the load balancer endpoint. Consider deploying highly-available Unleash Edge instances as intermediaries. Edge caches flags locally, improving performance and resilience.
This configuration mitigates single points of failure for the Unleash API server and its database within a region.
Monitoring and observability
Unleash Cloud provides built-in observability dashboards, usage metrics, and system status updates via the Admin UI and a public status page.
Underlying infrastructure monitoring, alerting, and scaling are handled by Unleash SREs.
Use the Connected Edges dashboard to get observability metrics for Unleash Edge instances, such as ID, region, resource usage, and latency.
Unleash is architected with scalability, performance, and resilience in mind, designed specifically for supporting demanding enterprise workloads. With fast, local feature flag evaluations, Unleash Edge for added scalability, and flexible deployment models, organizations can achieve reliable, high-performance feature management at a global scale, enabling faster, safer software delivery.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
This FAQ section addresses common questions about scaling Unleash for enterprise use, focusing on performance, high availability, and managing large user and flag volumes.
Should I choose cloud-hosted or self-hosted Unleash?
Choosing a hosting option depends on several factors such as: your organization’s tolerance for operational overhead, requirements for data residency and infrastructure control, regulatory compliance needs (such as FedRAMP), available SRE/DevOps resources and expertise, and desired speed of implementation (time-to-value).
We generally recommend Unleash Cloud for most enterprises due to reduced operational complexity, built-in high-availability and disaster recovery, and managed scaling by Unleash experts. Choose self-hosted or hybrid if specific control, network isolation (air-gapped), or strict regulatory requirements mandate it.
How does Unleash ensure fast feature flag checks without slowing down user experience?
Unleash achieves speed primarily through how feature flag evaluation works in the SDKs.
- Local evaluation: Your application integrates an Unleash SDK. This SDK periodically fetches flag configurations from the Unleash API or Unleash Edge. In Backend SDKs, the evaluation of which flags apply to a specific user happens instantly within your application’s memory using the fetched rules and the context you provide (like user ID, location, etc.). Frontend SDKs can rely on Unleash Edge for fast feature flag evaluation.
- No network calls per flag check: Because evaluation is local, there’s no network latency added for each feature flag check during a user’s request processing. This makes flag evaluation extremely fast.
- SDK caching: SDKs securely cache the latest known flag configuration. This ensures evaluations continue even if the connection to Unleash is temporarily lost.
How does Unleash handle scaling for potentially tens of millions of users and sudden traffic peaks (like a product launch or marketing campaign)?
Unleash Cloud is architected on AWS for high availability and elasticity:
- Multi-AZ deployment: Services run across multiple Availability Zones within a region for fault tolerance.
- Auto scaling: We use load balancers and auto-scaling groups for the Unleash API instances, automatically adjusting capacity based on real-time traffic load.
- Managed databases: Highly available managed databases with hot standbys and automatic failover are used.
- Global Edge network: Unleash Edge distributes flag serving globally for low latency and high throughput with a low memory footprint.
- Proactive monitoring and elasticity: We continuously monitor performance and scale resources proactively to handle anticipated and sudden peaks smoothly.
- Disaster recovery: Full backups and a running cluster exist in a separate region for rare regional failure scenarios.
What is Unleash Edge and why would I need it?
Unleash Edge is a lightweight, globally distributable, read-only cache for your feature flag configurations. Think of it as a specialized distribution layer for feature flags. You need it primarily for:
- Low latency: Serving flags from an Edge instance geographically closer to your users/applications drastically reduces lookup times, especially critical for frontend/mobile apps.
- Scalability: Edge handles the high volume of SDK requests, offloading the Unleash API server and database, allowing the system to scale to millions of connections.
- Availability: Edge caches configurations and continues serving them even if the Unleash API server is temporarily unavailable, adding another layer of resilience beyond the SDK cache.
What are the key challenges of self-hosting Unleash at scale?
The main challenges include:
- Database management: Scaling, ensuring high availability, performing backups/restores, and optimizing performance for the stateful database component.
- High availability: Architecting and managing redundancy for all components across multiple AZs or even regions.
- Global Edge deployment: If needed, deploying, managing, routing traffic to, and monitoring Edge instances across multiple geographic locations adds complexity.
- Monitoring and alerting: Setting up comprehensive monitoring for all components and configuring meaningful alerts requires significant effort.
- Operational maintenance: Handling upgrades, security patching, dependency management, and capacity planning requires dedicated SRE/DevOps resources.
What happens if the Unleash API goes down? Will my application stop working?
No, your application will not stop working. The Unleash SDKs are designed for resilience:
- Cached configuration: The SDK will continue operating using the last successfully fetched set of feature flag rules stored in its cache.
- Default values: You define default values for flags within your code, which the SDK can use if it has no cached configuration or if a specific flag isn’t present in the cache.
- Unleash Edge: Using Unleash Edge provides an additional layer of availability, serving flags even if the Unleash API server is down.
You can monitor the status via our public status page.
Why use Unleash Edge instead of just putting the main Unleash API in an Auto Scaling Group (ASG)?
While ASGs scale the Unleash API server, Edge solves different problems:
- Global latency: ASGs don’t solve latency for users far from the API’s region. Edge brings flags geographically closer.
- Unleash API resilience: If the Unleash API server or its database has issues, all instances in the ASG might be affected. Edge instances can continue serving cached flags independently during such an outage.
- Load distribution: Edge is optimized specifically for the high-volume, read-heavy load from SDKs, protecting the Unleash API server (which handles writes, UI, and configuration logic).
Can Edge run in air-gapped environments?
Yes, self-hosted Unleash Edge can operate effectively in restricted or air-gapped environments. Once synced with an accessible Unleash API server (which could also be self-hosted within the restricted network), Edge can serve cached flags locally even if disconnected, synchronizing again when connectivity is restored.
Unleash Edge vs. Unleash Proxy: What’s the difference?
Unleash Edge is the modern, high-performance, recommended successor to the legacy Unleash Proxy. Edge offers significant improvements in performance, scalability, real-time updates (via streaming in Enterprise Edge), and maintainability compared to the older Proxy component. New deployments should use Unleash Edge.
How does Unleash handle service outages?
Unleash Cloud is designed for high availability:
- Within a region: Automatic failover across multiple Availability Zones for components like the API server and database. Managed database failover typically completes in under 2 minutes.
- Regional outages: A comprehensive disaster recovery strategy involves regular backups and the capability to restore service in a secondary backup region in the rare event of a complete primary region failure.
How much traffic can Unleash handle?
Unleash is extremely scalable, designed to handle traffic volumes well beyond typical enterprise needs, as detailed in our recent performance test updates.
The exact capacity depends on the evaluation method:
- Backend SDKs: Flags are evaluated locally in your application, scaling as your application does. A single small Unleash instance can support 7,500 connected SDKs, enabling a 750 trillion evaluations per day across those connected applications. You can scale further by adding more Unleash instances.
- Frontend SDKs with Unleash Edge: Unleash Edge handles flag evaluations and scales horizontally. Performance tests showed 5 Edge instances handling over 11,000 requests per second (RPS), and a single instance configuration capable of managing at least 864 million requests daily.